Ferrous and nonferrous are the main classifications of metals. The main difference between ferrous and nonferrous metals is that ferrous metals contain iron while nonferrous metals do not. While iron contents are one differentiator, there are other properties that separate these metals from one another.
Find out How to Implement a VMI Strategy
What are Ferrous Metals?
Ferrous metals are metals that are made up of mostly iron. They are hard, durable, and strong. Most ferrous metals are magnetic, but some types of them are prone to rust and corrosion. Ferrous metals contain other metals, besides iron, and when mixed can yield different properties depending on the metal. These differing properties allow different alloys, or mixtures of metal, to be useful for different applications. For example, the chromium in stainless steel prevents the iron from rusting.
Benefits of Ferrous Metals:
- Most ferrous metals are magnetic
- Wear Resistant
- Low Melting Point
- Cost Effectiveness
- Recyclable
Types of Ferrous Metals:
Steel
Steel is produced by iron and carbon together resulting in a hardened version of iron. Steel is strong and durable, making it useful for construction industries as well as machinery and manufacturing industries.
Stainless Steel
Stainless Steel is one of the most durable ferrous metals and has a better life-long value than most steels because it is heat and corrosion-resistant.
Cast Iron
Cast iron is easily molded and can be cast into a variety of shapes. It is hard and resistant to wear, making it mainly used for cookware, water pipes, machine tools, and engines.
Carbon Steel
Carbon Steel is iron mixed with increased carbon compared to steel, making it exceptionally hard and durable. It is mainly used for manufacturing tools such as drills and blades.
Wrought Iron
Wrought iron is almost made of pure iron. It contains less carbon than most ferrous metals. This makes it less corrosive but still vulnerable. Wrought iron is used for railings, gates, chains, and agricultural tools.
What are Nonferrous Metals?
Nonferrous metals are lightweight, nonmagnetic, highly conductive, and more resistant to corrosion. Nonferrous metals are more expensive than ferrous metals because they are more complex to produce. These metals are used in a variety of industrial, commercial, and residential applications. Non-ferrous materials are lightweight, softer, and malleable.
Benefits of Nonferrous Metals:
- Easy to Fabricate
- Low Density (less mass)
- High Resistance to Corrosion
- Great Electrical Conductivity
- Recyclable
Types of Nonferrous Metals:
Copper
Copper is a bright color, that is highly malleable and conductive. Because of its conductivity, it can be used to make electrical wires. Its malleability allows it to be easily shaped without cracking, making it useful for creating statues and manufacturing piping.
Aluminum
Aluminum is soft and lightweight, making it easy to work with. It’s ideally used for fast manufacturing to produce aircraft components, car parts production, food cans, and much more.
Lead
Lead is very heavy but soft and malleable. It is used for a lot of protective piping because it is very resistant to corrosion from water and acids, like the piping in power cables or batteries.
Other Metals
Other nonferrous metals include zinc, tin, brass, precious metals like gold, silver, platinum, and much more.
Main Differences Between Ferrous and Nonferrous Metals
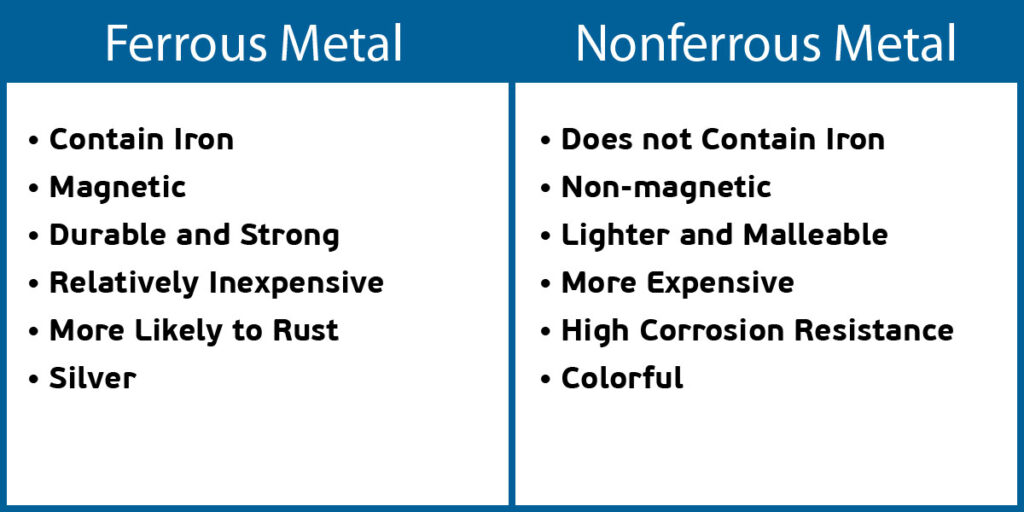
Metals are classified into two groups, ferrous and nonferrous. However, these differences in this classification go much further than the presence and absence of iron. These metals differ in terms of strength, magnetism, and resistance to corrosion, which affects the weldability and applicability of these metals. There are numerous factors to consider before choosing a metal, understanding the differences will help you determine the correct metal for your project.





